- October 18, 2023
- Posted by: Henry Chrizostom
- Category: Cyber security

Introduction:
With technology advancing faster than ever, cybersecurity has become a paramount concern for organisations. Simply relying on technical security controls like firewalls and encryption is no longer enough to protect sensitive data. Social engineering, which exploits human psychology to gain unauthorized access or sensitive information, is a significant threat. This blog post delves into social engineering, its tactics, and how to protect yourself and your organization.
What is Social Engineering?
Social engineering is a dangerous threat that exploits human nature. These malicious attacks aim to deceive users and trick them into making security mistakes or giving away confidential information. Attackers use psychological manipulation to gain the trust of their victims, offering incentives to break security practices.
Is your organization prepared for social engineering attacks, and do you prioritize it as a risk?
2022 Reports detailing the consequences of social engineering continue to be alarming.
· 98% of Cyber Attacks Involve Some Form of Social Engineering. – Source: Purplesec]
· Up to 90% of Malicious Data Breaches Involve Social Engineering – [Source: KnowBe4]
· 84% of Organizations Fell Victim to a Phishing Attack in 2022 [Source: Proof Point]
· Social Engineering Attacks Cost Companies $130,000 On Average [Source: Security Info Watch]
Successful Social Engineering doesn’t happen overnight. It involves a series of steps.
Let’s explore the thought process of hackers (Social Engineering Life Cycle).
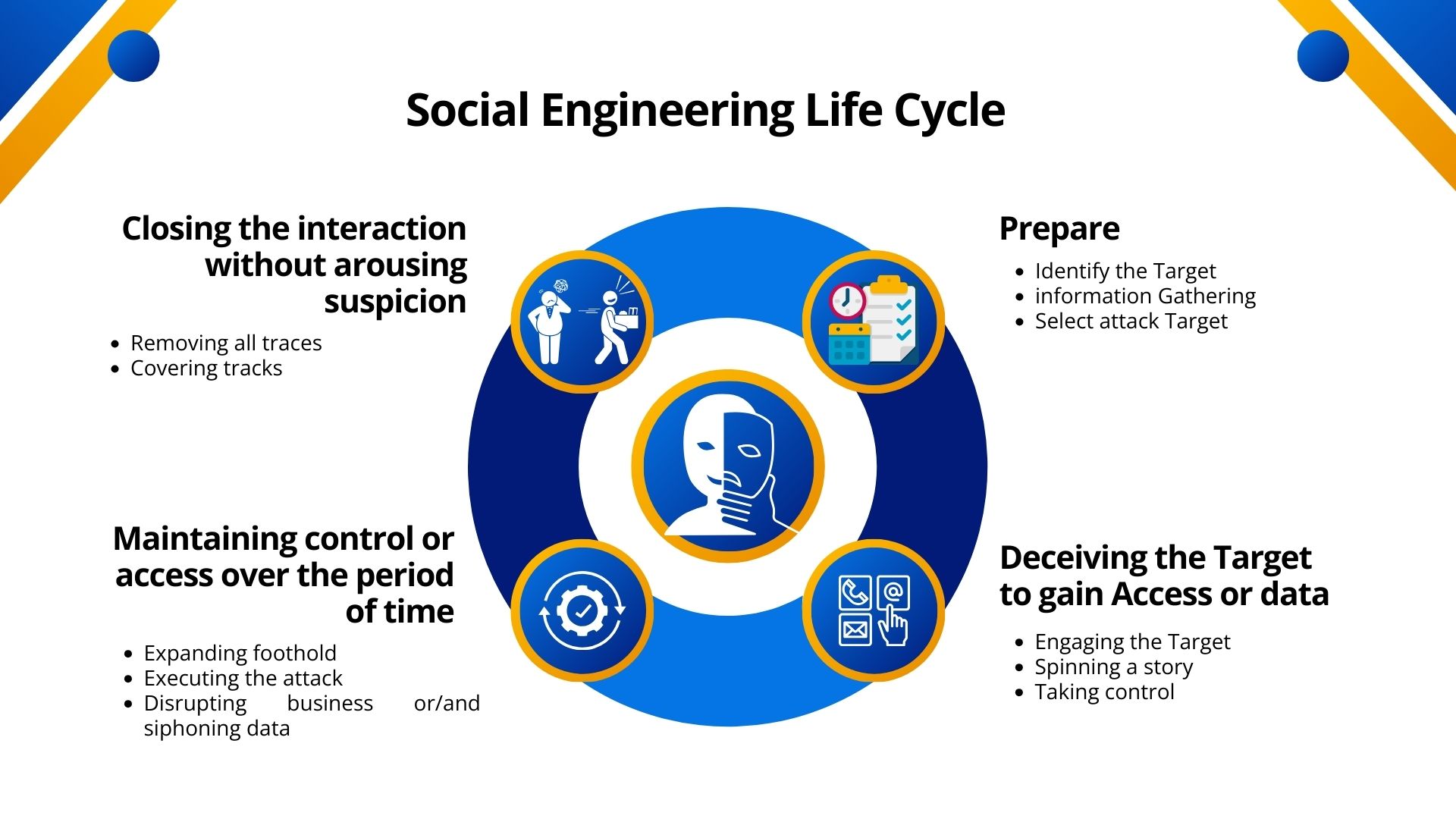
Common Social Engineering Tactics:
Phishing Attacks:
Phishing emails are fraudulent emails that claim to be from trusted sources but are actually sent by malicious individuals to steal personal information. There are many types of phishing scams in which an attacker will try to manipulate recipients into sharing sensitive information or taking some other damaging action, as follows.
Spear Phishing
A targeted cyber-attack focuses on individuals with privileged access to sensitive information, computer networks, or corporate funds. Scammers research the target, often using social media profiles, and create a convincing message to access the target’s information.
Whale Phishing
Spear phishing targets high-profile individuals, like CEOs or politicians.
Business Email Compromise (BEC)
Hackers use compromised credentials to send fraudulent emails from the victim’s actual account, making it harder to detect.
Vishing
Phone phishing, also known as vishing, is an online fraud where attackers use phone calls to trick people into providing personal information. The caller may pretend to be calling on behalf of the government or tech support for well-known companies. Bank impersonation is another common phone phishing scam.
Clone Phishing
Attackers clone a real email message with attachments and resend it, pretending to be the original sender. The attachments are replaced with malware but look like the original documents.
An example is fake emails from trusted companies like PayPal or Amazon that urge you to log in immediately by clicking a link. The goal is to trick you into providing personal information like login credentials or credit card details. Always be cautious and verify emails before clicking links.
How to Detect phishing emails
According to the Proof Point Report 2022, 84% of organisations have fallen victim to a phishing attack. In this article, we will explore an example of a suspicious email and highlight six areas you should be aware of when reading your email.
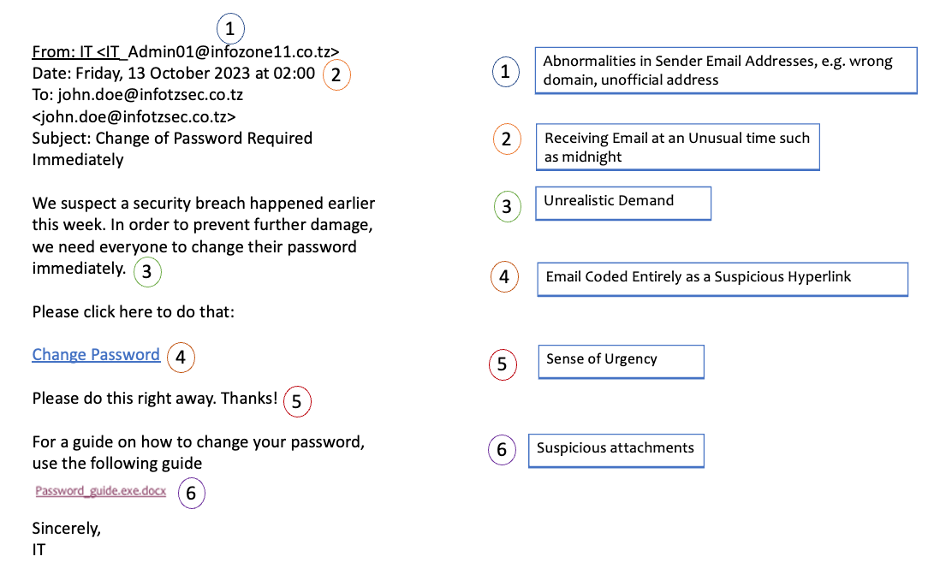
Pretexting:
Pretexting attacks involve threat actors posing as someone else and tricking victims into sharing sensitive information. This information is then used to carry out secondary attacks or identity theft.
Pretexting attacks deceive individuals to exploit an organization’s weaknesses. Attackers pretend to be someone they are not like IT services auditors or HR personnel in finance. They create a believable story to gain the victim’s trust and extract sensitive information. Unlike phishing attacks, which exploit fear, these attacks require careful planning and can be very dangerous.
Tailgating and Piggybacking:
Have you ever helped to open the door to a workplace, thinking they are one of you because of wearing smart clothes? Most of us have fallen into this trap because of the trust and need to help others. Tailgating and piggybacking are in-person social engineering tactics that unauthorised people use to access restricted physical locations protected by electronic systems designed to limit access.
We need to have strong physical security measures; visitors should always be escorted. Gaining access to restricted areas in the company will enable the perpetrator to gain access to sensitive information or install a malicious device that will make it easy for others to penetrate the critical networks.
Baiting:
Baiting is a tactic to deceive victims by making fraudulent promises that trigger their curiosity or greed. This can include enticing offers that invite people to purchase items at a discounted price or even for free, while simultaneously tricking them into sharing sensitive information. Victims should be wary of these tactics and exercise caution before providing any personal information.
In one scenario, a hacker may create a fraudulent website that closely mimics a legitimate business, and lure unsuspecting victims into submitting their credit card details in exchange for products or services. In another scenario, an attacker may deliberately leave a USB drive containing malicious software in a public area, such as a lobby or a parking lot, hoping that someone will pick it up and plug it into their device out of curiosity, thereby triggering the payload.
Scareware
Scareware preys on unsuspecting users by bombarding them with false warnings and fake threats. They trick you into believing that your computer is infected with malware and urge you to download software that claims to help. However, this software is either completely useless or even worse, malware itself. This type of attack may also be referred to as deception software, rogue scanner software, or fraudware. Don’t fall for this treacherous tactic – stay alert and protect yourself from Scareware.
Don’t fall victim to scareware! You may come across seemingly legitimate pop-up banners while browsing the web, displaying alarming messages like “Your computer may be infected with harmful spyware programs.” Beware! These pop-ups may offer to install a tool, which could be infected with dangerous malware, or direct you to a malicious website that could infect your computer. Don’t take the bait! Stay vigilant and avoid clicking on suspicious links or downloading any unknown software. Protect your computer and yourself from potential harm by being cautious of any such pop-ups.
Quizzes and Surveys:
Social engineers can use quizzes and surveys to compile detailed profiles of individuals, which they then use in spear-phishing or identity theft schemes. By examining responses, they can identify trends, preferences, and habits to manipulate emotions and exploit psychological weaknesses.
This highlights the importance of being cautious when sharing personal information online. Do your employees know how to stay safe and vigilant while they are online?
Protecting Against Social Engineering:
Tactics and best practices to prevent Social Engineering should be aware to everyone. Let us explore some of the best practices to follow:
|
Security Control |
Benefit |
| Employee Cyber Security Training and Awareness: Design a Cyber Security Awareness program that will be issued through various channels such as emails, office posters/magazines, and organized virtual or physical training. | Raise employees’ awareness of social engineering techniques and always stay vigilant in the Digital Age |
| Simulated phishing exercises: This aims to test individuals’ understanding and reaction to social engineering attacks, complementing training and awareness programs. | Assessing employees’ knowledge of social engineering and their reactions to it is important. This will help identify weak areas where additional training is needed. |
| Implementing Strong Access Controls: It is crucial to deploy a range of security measures to protect against social engineering attacks, which can compromise sensitive information. These may include email security solutions, perimeter firewalls, web filtering solutions, and endpoint security solutions. | By implementing such measures, we can reduce the risk of social engineering attacks and prevent any potential damage. |
| Physical security measures: Physical security measures such as guards, gates, biometric or card access, lightning and video cameras should be implemented to ensure only authorized personnel are allowed physical access to the building. | Physical access should be restricted to authorized personnel. Weak points can be identified for targeted protection. |
| Multi-factor authentication and strong password policies: Protecting your account is your top priority. That’s why a multi-step login process that goes beyond just a password should not be an option. By requiring additional information, such as a code sent to your email, a secret question, or a fingerprint scan, can ensure that your information is safe and secure.
When using critical applications or social media, use multi-factor authentication to enhance access control. |
Multi-step login process makes it difficult for hackers to take control of the whole authentication process (1st and 2nd authentication mechanisms) |
| Regular Security Audits and Assessments:As technology continues to evolve rapidly, security remains a moving target. It is mandatory to regularly assess physical security measures, access controls, and employee resilience to social engineering to identify weak areas that require improvement. | This helps identify weaknesses and critical areas needing the most protection.In this way, organizations can remain vigilant against social engineering attacks and respond proactively. |
How do you respond to Social Engineering:
Social engineering attacks can strike at any time, despite our best efforts to prevent them. It’s essential that users and employees know how to respond if they suspect their accounts have been compromised. Cybersecurity awareness training is the key to teaching them how to report and react to such attacks in the following way.
- Change the password of the compromised account immediately
- Report the incident to the format channel that has been made aware to all employees e.g., spam@infosec.co.tz, Security Operation Center (SOC) reporting phone number
- Initiate Incident Response in case of an attack that negatively impacts e.g., a social engineering attack that leads to a ransomware attack, which encrypts critical sensitive data. This is done to recover from the attack and prevent further damage.
By investing in the training, you can empower your employees to be the first line of defense against cybersecurity threats. Don’t wait until it’s too late – make cybersecurity awareness training a priority today.
Conclusion:
In today’s world, where technology is a double-edged sword, it is crucial to comprehend and protect against social engineering attacks. By integrating technological defenses with comprehensive training and awareness initiatives, individuals and organizations can build a strong defense against this widespread threat.
Knowledge is the most powerful weapon in the fight against social engineering. Stay informed and vigilant to fortify our digital fortresses.
Infosec’s Cyber Security Awareness Program
To help your organization with Cyber security Transformation, Infosec have a special cyber security awareness service. We conduct scenario-based Cyber security awareness and tabletop exercises, these tailored awareness targets employees, executives, and boards of directors.
Infosec also engages VIP/Celebrities/Executives in a paid personal Cyber Security advisor role.
Book your slot through info@infosecltd.com or Whatsapp at +255673240533

